Formatting a hard disk drive (HDD) is a process that involves preparing the storage device for use by an operating system (OS) by erasing all existing data and setting up a file system. This process can be essential for various reasons, such as installing a new OS, repurposing an old drive, or resolving data corruption issues. Here's a comprehensive guide to formatting an HDD, covering the steps, considerations, and best practices.
What is Formatting?
Formatting is the process of preparing a storage device, such as an HDD, for data storage. It involves:
Partitioning: Dividing the drive into sections that the OS can manage individually.
File System Setup: Creating a structure that allows the OS to read and write data efficiently. Common file systems include NTFS (Windows), HFS+ (Mac), and ext4 (Linux).
Types of Formatting
Quick Format: Erases the file system table and reinitializes the file system, making the drive appear empty. It does not erase the data securely, which can be recovered using specialized software.
Full Format: Scans the disk for bad sectors, erases all data, and writes zeros to the entire disk. It is more thorough and secure than a quick format.
Preparing for Formatting
Backup Important Data
Before formatting, ensure that you back up all important data. Formatting will erase all data on the drive, and recovery can be difficult or impossible.
Choose the Right File System
Select the appropriate file system based on your needs:
NTFS: Suitable for Windows systems. Supports large files and drives.
FAT32: Compatible with multiple OSes, but limited to 4GB file sizes.
exFAT: An improvement over FAT32. supports large files, and is compatible with most OSes.
HFS+: Optimized for macOS.
ext4: Commonly used in Linux systems.
Formatting an HDD in Windows
Using Disk Management
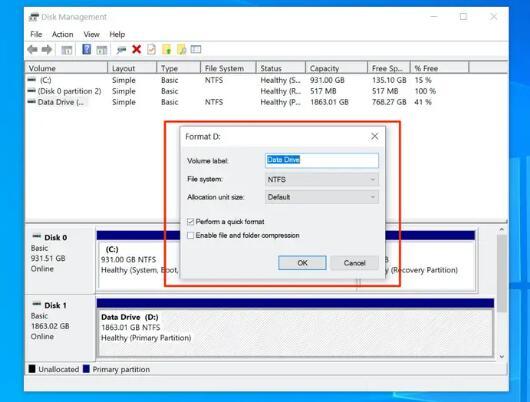
Open Disk Management: Press Win + X and select Disk Management.
Select the Drive: Right-click on the drive you want to format and choose Format.
Choose Options: Set the volume label, file system (e.g., NTFS), and allocation unit size.
Start Formatting: Click OK to begin the formatting process. Confirm any prompts.
Using Command Prompt
Open Command Prompt: Press Win + X and select Command Prompt (Admin).
List Disks: Type diskpart and press Enter, then list disk to display connected drives.
Select Disk: Type select disk X (replace X with the drive number).
Clean Disk: Type clean to remove all partitions.
Create Partition: Type create partition primary.
Format Disk: Type format fs=ntfs quick (or another file system as needed).
Assign Drive Letter: Type assign letter=X (replace X with the desired letter).
Formatting an HDD in macOS
Using Disk Utility
Open Disk Utility: Go to Applications > Utilities > Disk Utility.
Select the Drive: Choose the drive you want to format from the sidebar.
Erase: Click the Erase button.
Choose Options: Set the name, format (e.g., APFS, Mac OS Extended), and scheme (GUID Partition Map).
Start Formatting: Click Erase to begin the process. Confirm any prompts.
Formatting an HDD in Linux
Using GParted
Install GParted: If not already installed, use your package manager to install it.
Open GParted: Run sudo gparted from the terminal.
Select the Drive: Choose the drive from the dropdown menu in the top right.
Unallocate Space: Right-click on any existing partitions and choose Delete.
Create New Partition Table: Go to Device > Create Partition Table.
Create New Partition: Right-click on the unallocated space, select New, choose the file system (e.g., ext4), and apply changes.
Using Command Line
Open Terminal: Access the terminal.
List Disks: Use lsblk to list connected drives.
Partition Disk: Use fdisk /dev/sdX (replace X with the drive letter).
Create Partition Table: Press o to create a new DOS partition table.
Create Partition: Press n to create a new partition, then follow the prompts.
Write Changes: Press w to write changes and exit.
Format Partition: Use mkfs.ext4 /dev/sdX1 (replace X1 with the partition).
Post-Formatting Considerations
Data Security
If the drive contains sensitive data, consider using a full format or additional tools like DBAN (Darik's Boot and Nuke) to securely erase data.
Health Check
Run disk utility tools to check the health of the drive. Tools like CrystalDiskInfo (Windows), Disk Utility (macOS), and smartctl (Linux) can provide detailed health reports.
Partitioning for Efficiency
Consider creating multiple partitions for different types of data. This can improve organization and may enhance performance.
Troubleshooting
Common Issues
Drive Not Recognized: Ensure the drive is properly connected and check BIOS/UEFI settings.
Formatting Errors: Try using different methods or tools. Check for hardware issues.
Slow Performance: Perform a disk health check. The drive may have bad sectors or be failing.
Recovery
If formatting fails or data needs to be recovered, tools like Recuva (Windows), Disk Drill (macOS), and TestDisk (Linux) can help retrieve lost data.
Formatting an HDD is a straightforward process when the proper steps are followed. It is crucial to back up important data, select the appropriate file system, and use the correct tools for your OS. By understanding the nuances of formatting and post-formatting considerations, you can ensure your HDD is prepared for efficient and reliable use.